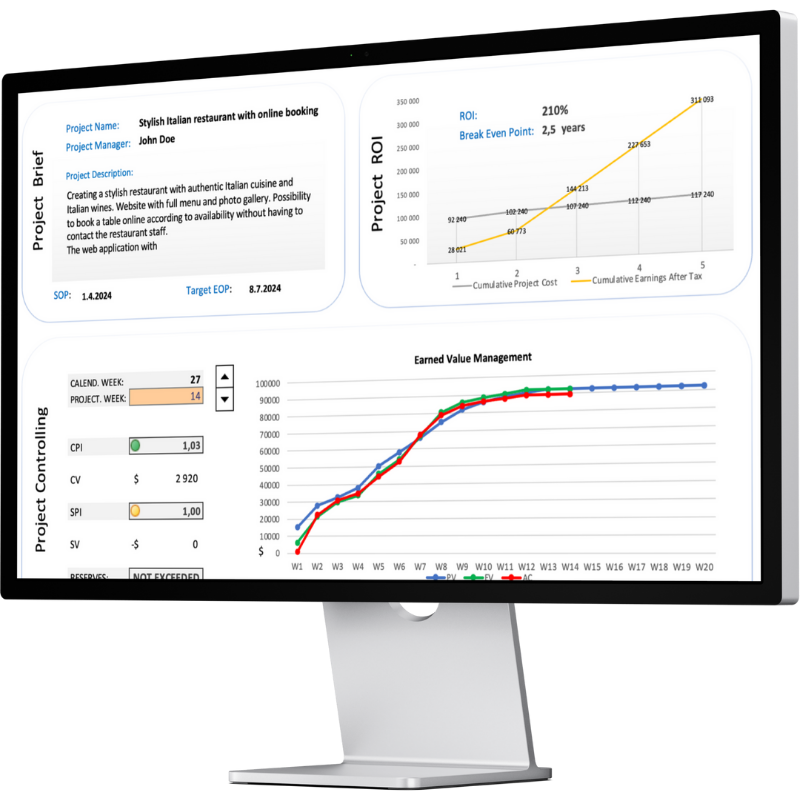
One-pager providing an overview of all key project indicators and current project status, including ROI, CPI, SPI, open risks, and open deviations.
Full project scope description. The document must be agreed upon and approved by all stakeholders, authorizing the project manager to utilize corporate resources and initiate the project.
Risk assessment is directly linked to sources of risk, such as SWOT analysis and other independent resources, with risk severity evaluation, planned mitigation actions integrated into project planning, automated task status updates. Residual risk evaluation.
The Project Baseline is the initial project plan used to define the project budget, including the schedule and the calculation of all variable and fixed costs.
An overview of all foreseen fixed costs that are planned and gradually updated during the project. These costs are automatically transferred to the project plan and to project controlling such as EVM.
Our advance Project Gantt Chart for easy planning and updating of all tasks in one place. In this plan, inputs from all linked templates are implemented and the status of execution is carried back. The interconnectedness of all the different project management components makes this template system unique.
ROI (Return on Investment) in project management measures the financial benefit gained from a project relative to its cost, indicating project profitability and value creation. Break even point is calculated to show when the project becomes profitable.
EVM (Earned Value Management): A project management method that integrates scope, schedule, and cost to assess project performance and progress.
CPI (Cost Performance Index): A measure of cost efficiency in a project, calculated as the ratio of earned value (EV) to actual cost (AC); CPI > 1 indicates cost efficiency.
SPI (Schedule Performance Index): A measure of schedule efficiency, calculated as the ratio of earned value (EV) to planned value (PV); SPI > 1 indicates the project is ahead of schedule.
Complications and deviations from the original plan accompany every project. Deviation management and full integration of corrective actions into the project plan is critical to successful project implementation. The status of implementation is fed back from the deviation list.
The template contains a comprehensive description of all template fields and instructions for using the template. For example, it is important to follow the correct procedure when inserting new rows into the scheduling process so as not to break the formulas that provide and automate the entire scheduling process.


